Source: Springer Link
Abstract
Background
New York City emerged as an epicenter of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Objective
To describe the clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with mortality in a large patient population in the USA.
Design
Retrospective cohort study.
Participants
6493 patients who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 with clinical outcomes between March 13 and April 17, 2020, who were seen in one of the 8 hospitals and/or over 400 ambulatory practices in the New York City metropolitan area
Main Measures
Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality.
Key Results
A total of 858 of 6493 (13.2%) patients in our total cohort died: 52/2785 (1.9%) ambulatory patients and 806/3708 (21.7%) hospitalized patients. Cox proportional hazard regression modeling showed an increased risk of in-hospital mortality associated with age older than 50 years (hazard ratio [HR] 2.34, CI 1.47–3.71), systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg (HR 1.38, CI 1.06–1.80), a respiratory rate greater than 24 per min (HR 1.43, CI 1.13–1.83), peripheral oxygen saturation less than 92% (HR 2.12, CI 1.56–2.88), estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 60 mL/min/1.73m2 (HR 1.80, CI 1.60–2.02), IL-6 greater than 100 pg/mL (HR 1.50, CI 1.12–2.03), D-dimer greater than 2 mcg/mL (HR 1.19, CI 1.02–1.39), and troponin greater than 0.03 ng/mL (HR 1.40, CI 1.23–1.62). Decreased risk of in-hospital mortality was associated with female sex (HR 0.84, CI 0.77–0.90), African American race (HR 0.78 CI 0.65–0.95), and hydroxychloroquine use (HR 0.53, CI 0.41–0.67).
Conclusions
Among patients with COVID-19, older age, male sex, hypotension, tachypnea, hypoxia, impaired renal function, elevated D-dimer, and elevated troponin were associated with increased in-hospital mortality and hydroxychloroquine use was associated with decreased in-hospital mortality.
INTRODUCTION
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a pandemic that has impacted medical systems, societies, and economies worldwide. The first case of COVID-19, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 virus (SARS-CoV-2)1, was reported in China in December 20192. The virus has spread globally at a rapid pace, resulting in more than 2 million confirmed cases as of April 17, 20203. In recent weeks, New York City has emerged as an epicenter of the pandemic, with over 120,000 confirmed cases and over 13,000 deaths due to confirmed or probable COVID-19 death as of April 17, 20204. Studies of the clinical characteristics and epidemiologic characteristics of COVID-19 have been conducted in countries experiencing outbreaks earlier than the USA5,6,7,8,9,10,11. Large-scale observational data of the clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in the population of the USA are scarce. In this study, we describe the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in ambulatory and inpatient settings and identify risk factors associated with mortality in hospitalized patients.
METHODS
Study Design and Participants
A multicenter retrospective cohort study of patients with COVID-19 patients was conducted using the medical records of the Mount Sinai Health System, a large urban health system of 8 hospitals and more than four hundred ambulatory practices in the New York City metropolitan area. Patients with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result and an encounter with a healthcare provider for COVID-19 between March 12 and April 17, 2020, were included in this study. A confirmed case of COVID-19 was defined as a positive result on reverse-transcriptase–polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR) assay of nasopharyngeal swab specimens. The study population was dichotomized into ambulatory and hospitalized groups. The former included patients whose encounter was an office visit, emergency department (ED) visit, or telehealth/telemedicine. Inpatients and ambulatory patients who were subsequently admitted to the hospital were included in the hospitalized group.
Both groups were further subdivided into survivors and non-survivors. Ambulatory non-survivors were patients who had expired prior to presentation to the ED, who had expired in the ED prior to admission to the hospital units, or who had an office or telemedicine encounter and were later found out to be deceased. Ambulatory survivors included all other ambulatory patients. Hospitalized non-survivors were patients who had expired as of April 17, 2020. Hospitalized survivors were patients who had been discharged home or to other facilities as of April 17, 2020.
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has waived informed consent and Institutional Review Board approval because the study used a de-identified database.
Definitions
The following covariates were extracted from the database: patients’ age, sex, ethnicity, race, smoking status, vital signs including temperature, peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2), heart rate, respiratory rate (RR), blood pressure (BP), body mass index (BMI), and laboratory results including white blood cell count (WBC), D-dimer, interleukin-6 (IL-6), hemoglobin, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin, ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), fibrinogen (FBG), interleukin-6 (IL-6), comorbidities, and treatments.
Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were reported as median with interquartile range. Categorical variables were expressed as proportions. Temporary changes of vital signs and laboratory values in survivors and non-survivors for the first 14 days after admission were assessed. To illustrate the risk associated with changes in the continuous variables, including vital signs and laboratory values, multivariate generalized additive models were used to calculate the odds ratio (OR) for mortality, with each median value set as a reference (i.e., OR = 1). The hazard ratio (HR) of each variable for mortality risk was assessed using univariate Cox proportional hazard regression model. To account for missing data values for laboratory results, we introduced multiple imputation, which is a procedure used to replace missing values with other plausible values by creating multiple filling-in patterns to avert bias caused by missing data. Using the dataset with imputed values, univariate and multivariate Cox model were fit to calculate HR.
The multivariate Cox model was adjusted for the following variables assessed in the univariate Cox model: patients’ age, sex, race, cigarette use history, past medical history of asthma, hypertension, diabetes, or cancer, systolic BP, RR, SpO2, BMI, initial laboratory values (lymphocyte proportion, D-dimer, IL-6), and hydroxychloroquine use. For this Cox regression analysis, we excluded variables from the univariable analysis if their between-group differences were not significant, if the number of events was too small to calculate hazard ratios, or if they had collinearity with other significant values. Each hospital was considered by the clustering term in the Cox proportional hazard model analysis where the clustering effect associated with hospitals was accounted for by the robust sandwich estimator. Preliminary confirmation of predictability of the Cox proportional hazard model demonstrated the area under the curve (AUC) to be 0.808 (95% CI, 0.790–0.825, Supplementary Figure 1). To investigate the effect of hydroxychloroquine while addressing the imbalance among treatment groups, we introduced inverse probability weighting (IPTW) based on propensity scoring to control for observed differences in baseline characteristics between treatment group and control group. IPTW was calculated based on the same variables as used in the Cox regression models, except for hydroxychloroquine use. We then fitted an IPTW-adjusted Cox with doubly robust methods. Survival curves with stratification for hydroxychloroquine were constructed using the Kaplan-Meier method. All statistical analyses were performed using version 3.6.2 of the R programming language (R Project for Statistical Computing; R Foundation).
RESULTS
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
Between March 13 and April 17, there were 6493 confirmed COVID-19 cases, including 2785 (42.9 %) ambulatory patients and 3708 (57.1%) hospitalized patients. The demographics, clinical characteristics, and laboratory findings are shown in Table 1. The median age of the group was 59 (interquartile range [IQR] 43 to 72) with 66.6% of the patients older than 50 years of age. 45.5% of the patients were female. Based on patients’ self-reported race, 26.9% were white, 24.1% were African American, 4.4% were Asian, and 44.7% were other. Based on self-reported ethnicity, 57.5% were Non-Hispanic, 25.4% were Hispanic, and the rest were unknown or not reported.
Table 1 Clinical Characteristics of the Patients with COVID-19 Full size table
Ambulatory and Hospitalized Comparison
The median age was 47 years old in the ambulatory group (IQR 34 to 60) and 66 years old in the hospitalized group (IQR 55 to 78). 858 patients died (13.2%): 52 patients in the ambulatory group (1.9%) and 806 patients in the hospitalized group (21.7%). Among ambulatory patients, 69% were emergency room encounters without hospital admission, 18.2% were office-based encounters, and 1.4% were telemedicine encounters.
Compared with that of ambulatory patients, a higher proportion of hospitalized patients were older, were male, or had a history of cigarette use. Hospitalized patients were more likely to have coexisting medical conditions including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus (DM), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and cancer. Hospitalized patients were more likely to have abnormal vital signs and abnormal laboratory values including higher WBC count, lymphocyte, and neutrophil counts, higher levels of AST, CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, IL-6, LDH, D-dimer, and troponin, and lower levels of eGFR and hemoglobin. Clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients stratified by age group, gender, race, and hydroxychloroquine use are shown in Supplementary Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
Survivors and Non-Survivors
Clinical characteristics of the 2014 survivors and 806 non-survivors in the hospitalized group are shown in Table 2 (Supplementary Table 1 for the ambulatory group). The median number of days to discharge for survivors was 5 days (IQR, 3 to 9 days). The median number of days to death for non-survivors was also 5 days (IQR, 3 to 9 days). Compared with survivors, non-survivors were older and the higher proportion were male. Non-survivors were more likely to have a history of cigarette use and coexisting medical conditions including COPD, hypertension, DM, and CKD.
Table 2 Clinical Characteristics of the Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 Full size table
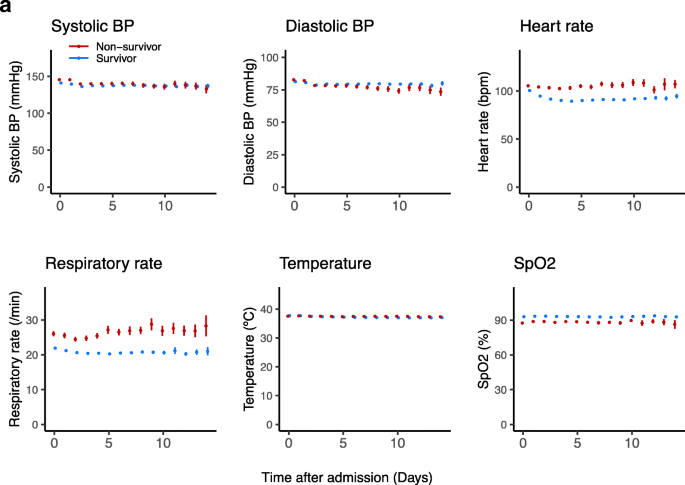
Temporal changes of vital signs and laboratory values in survivors and non-survivors during hospitalization are shown in Figure 1. Throughout hospitalization, non-survivors had higher heart rate and respiratory rate and lower oxygen saturation compared with survivors. Initial laboratory findings of non-survivors demonstrated higher WBC count and higher levels of D-dimer, IL-6, AST, CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, LDH, fibrinogen, and troponin. Throughout hospitalization, non-survivors had higher WBC count, neutrophil proportion, LDH, and ferritin levels, and lower eGFR and lymphocyte proportion. Non-survivors also had higher levels of CRP, D-dimer, and IL-6 in the first week of hospitalization. Non-survivors showed a marked increase in LDH, CRP, D-dimer, AST, ALT, and procalcitonin on day 1 after admission. Both groups had a trend of decreasing hemoglobin levels and increasing platelet counts during hospitalization; however, a more pronounced decrease in hemoglobin levels was seen in non-survivors, while an increase in platelet counts was greater for survivors. The generalized additive models demonstrated correlations between laboratory values and increased odds of in-hospital mortality which are similar to the difference observed between hospitalized survivors and non-survivors (Supplementary Figure 3).
Treatment
The majority of hospitalized patients received hydroxychloroquine (74.6% of survivors and 71.3% of non-survivors) and azithromycin (67.4% of survivors and 71.3% of non-survivors). Fewer hospitalized patients received other medications such as remdesivir, anakinra, tocilizumab, or sarilumab (Table 2). The majority of ambulatory patients did not receive hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin. Kaplan-Meier estimate showed lower mortality in hospitalized patients who received hydroxychloroquine (log rank P value < 0.001) (Supplementary Figure 4).
Risk Factors Associated with Mortality in Hospitalized Patients
The results of multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models are shown in Table 3 (univariate models are shown in Supplementary Table 6). Of 3708 hospitalized patients, 888 patients remained hospitalized as of April 7 and were not included in the analysis. In the multivariate analysis, factors associated with a higher risk of in-hospital mortality included age over 50, systolic blood pressure less than 90 mmHg, a respiratory rate greater than 24 per min, SpO2less than 92%, eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73m2, IL-6 greater than 100 pg/mL (6.5 times upper limit of normal [ULN]), D-dimer greater than 2 mcg/mL (4 times ULN), and troponin greater than 0.03 ng/mL. Factors associated with a lower risk of in-hospital mortality included female sex, African American race, and hydroxychloroquine use. The adjustment with IPTW did not lead to a significant change in the HR of hydroxychloroquine (without IPTW: HR 0.53, CI 0.41–0.67; with IPTW: HR 0.53, CI 0.41–0.68).
Table 3 Risk Factors Associated with In-Hospital Death Full size table
DISCUSSION
We report a large retrospective cohort study of both ambulatory and hospitalized patients with COVID-19 from across the New York City metropolitan area. The clinical characteristics described here represent the first large retrospective cohort study from the US population in a city at the epicenter of the pandemic.
Early reports showed that COVID-19 had a mortality rate among all confirmed cases of 2%12 which is significantly lower compared with that of 34% with MERS13 and 10% with SARS14. The mortality rate in hospitalized patients reported previously ranged from 4 to 28%2, 7,8,9, 11. The mortality rate of 25.9% among hospitalized patients in our study may be explained by more severe disease in our total cohort, by a different reporting method, or by geographic variation.
We identified several risk factors associated with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 that have been previously reported including older age and male sex. We report additional risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality including low SBP, tachypnea, low SpO2, low eGFR, and higher levels of IL-6, D-dimer, and troponin levels.
The severity of coronavirus infection in humans has been previously described to increase during viral clearance suggesting pathogenicity arising from host immune response15. Our study confirmed again that older patients with COVID-19 hospitalization are at significantly higher risk of mortality. We did not observe any independent association between in-hospital mortality and some of the common coexisting medical conditions including hypertension, diabetes, or cancer. However, using calculated GFR as a surrogate for CKD, we observed that decreased renal function was a risk factor for in-hospital mortality, a finding that is consistent with previous studies16.
IL-6 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines production are felt to be due to immune dysregulation rather than normal response to SARS-CoV infection17, 18. Our findings are consistent with this theory, and we observed elevated IL-6 as an independent prognostic risk factor, with higher levels in non-survivors. In hospitalized patients, we saw fluctuating IL-6 levels, with a significant increase seen on day 1 of admission and an increasing level trend that was more pronounced in non-survivors.
Thrombocytosis was associated with disease activity in SARS and was thought to be secondary to the direct effect of the virus or effect of inflammatory cytokines19. We observed a greater thrombocytosis during hospitalization in survivors than in non-survivors. A previous study of IL-6 in primates revealed that there is a dose-dependent response of thrombocytosis induced by IL-620. The discrepancy between high IL-6 levels and lack of thrombocytosis in non-survivors could be explained by endothelial damage and subsequent platelet consumption from viral infection, impaired platelet release from megakaryocytes in the lung, or direct impairment of hematopoiesis21. This may suggest that the absence of reactive thrombocytosis may portend a poor response to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Elevated D-dimer in COVID-19 patients has been described previously22, 23. We report in this study its independent association with an increased risk of in-hospital mortality. Abnormal D-dimer alone is non-specific; however, the higher elevation in non-survivors suggests that coagulopathy, particularly disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), may contribute to mortality in COVID-19.
One of the functional receptors for pathogenic human coronavirus such as SARS-CoV is angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)24, and these receptors are expressed in heart tissues25. This suggests that SARS-CoV-2 virus could directly affect the heart. Similar to the previous finding that showed an association of cardiac injury and a higher risk of in-hospital mortality26, we observed elevated troponin levels in hospitalized patients as a risk factor for increased mortality.
Hydroxychloroquine is an analog of chloroquine, a widely used anti-malarial with immunomodulatory effects27. In vitro studies have shown that hydroxychloroquine has activity against SARS-CoV-2 28. The clinical data of hydroxychloroquine in patients with COVID-19 come from small studies that have shown mixed results. Chen et al. randomized 30 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 to receive hydroxychloroquine 400 mg daily for 5 days or placebo and found that 86.7% of the hydroxychloroquine group and 93.3% of the control group had negative throat swabs29. Chen et al. randomized 62 patients to hydroxychloroquine or placebo and reported shortened time to clinical recovery, fever resolution, and cough improvement in the hydroxychloroquine group30. Mahevas et al. reviewed 181 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 data who received hydroxychloroquine 600 mg daily and reported no difference in outcomes, including in ICU admission and/or death at 7 days follow-up31. Another randomized trial of 150 hospitalized patients by Tang et al. did not show symptomatic improvement at 28 days or clearance of SARS-CoV-2 with hydroxychloroquine use32. We attempted to adjust for all known confounders between the groups who did and did not receive hydroxychloroquine using multivariate regression analyses and the IPTW method, which revealed that hydroxychloroquine use was associated with decreased risk of in-hospital mortality. Due to the inherent limitations of our retrospective study design, there was no conclusive determination on the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in patients with COVID-19. More robust studies such as randomized clinical trials are needed.
Our study has several limitations. First, we have no long-term follow up data for ambulatory and discharged patients; hence, the clinical outcome observed may not be reflective of the true eventual outcome, particularly in the ambulatory group. Second, we have patients who remained hospitalized at the time of our analyses and did not have our outcomes, such as discharge or mortality, and were excluded for our comparison of survivors and non-survivors. Third, due to limitations and local testing policy during the study duration, there are an unknown number of patients who were not diagnosed with COVID-19 because of a lack of severe symptoms and/or hospitalization. Fourth, we are not able to adjust for unknown confounders that may affect the true treatment effect. These limitations prevent any definitive conclusions on the efficacy of any treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
In this retrospective study of over 6000 ambulatory and hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the New York City metropolitan area, age, male sex, tachypnea, low systolic blood pressure, low peripheral oxygen saturation, impaired renal function, elevated IL-6, elevated D-dimer, and elevated troponin were found to be risk factors for mortality. Hydroxychloroquine use was associated with decreased mortality.
Related:
Moroccan Scientist: Morocco’s Hydroxychloroquine 82.5% Success Reveals European Failures

